Install Docker In macOS
If you are using macOS, you are supposed to prepare a virtual machine/service to host a real Linux instance, and then control it in the remote.
Currently, there are at least 2 solutions to achieve it.
Option One: Docker.app
If you are using macOS, you could follow this guide. Download an image, and drag to your 'Applications' folder, click and run.
Currently, both of them are working pretty fine.
- Kubernetes is only available in Docker for Mac 17.12 CE Edge and higher, on the Edge channel.
- Edge can not disable "Sending usage statistics"
- For more
Either of them could satisfy the requirements in this course.
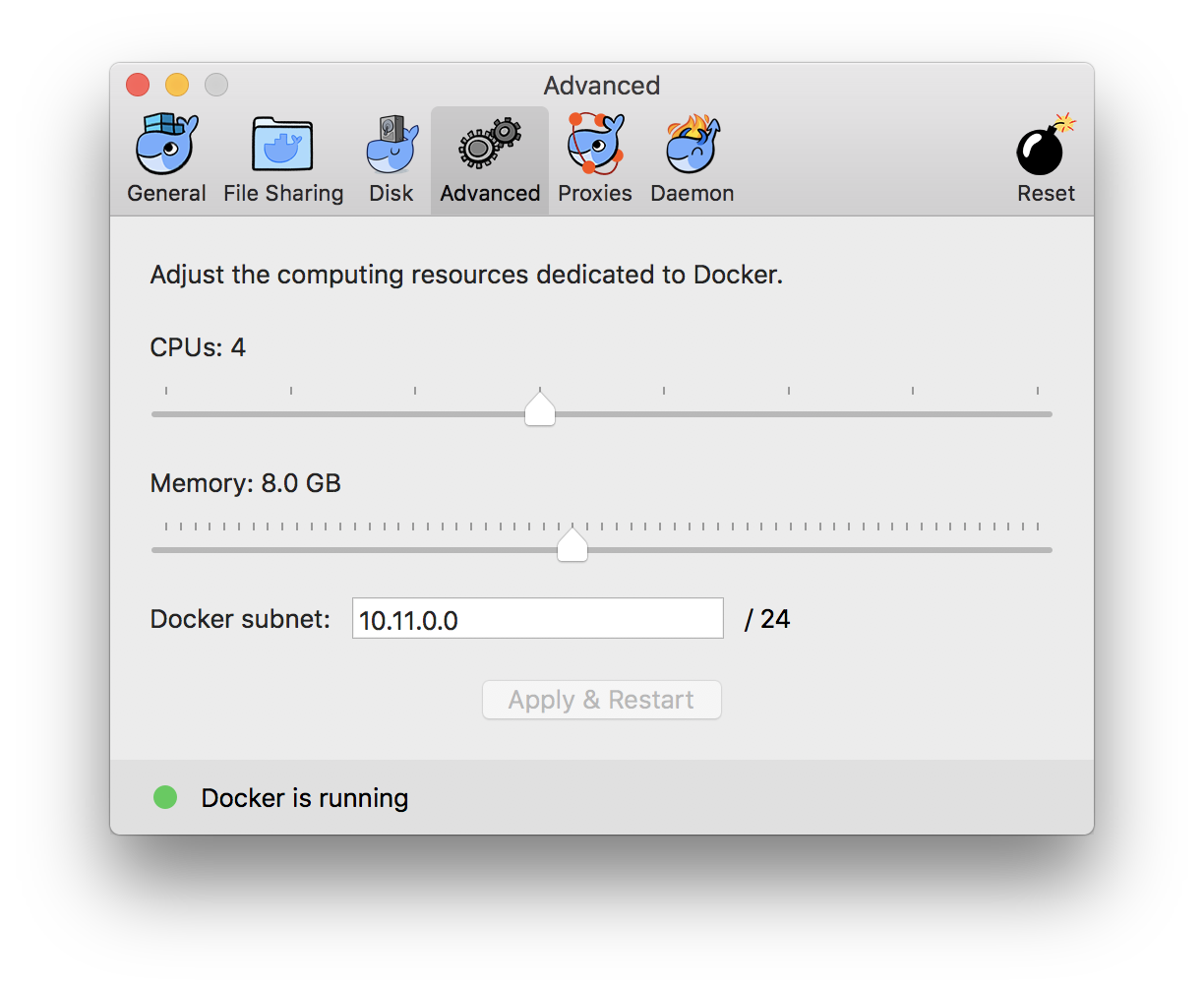
If you wish to host our image using Docker.app, you are supposed to click the icon for docker in the toolbar, and set the maximum memory to 4G-8G.
Docker.app requires sudo access, and the data will stored in $HOME/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker
Option Two: Homebrew + VirtualBox + Docker
However, here is an alternative solution.
First of all, you should make sure you have already installed HomeBrew.
Secondly, you are supposed to make sure your brew is up-to-date.
brew update # update brew repository
brew upgrade # update all packages for brew
brew doctor # check the status of your brew, it will provide some guide to make your brew be normal
Finally, you can install VirtualBox and Docker by using the following commands:
brew install Caskroom/cask/virtualbox
brew install docker-machine
brew install docker
To keep the Docker service active, we can use brew's service manager
$ brew services start docker-machine
==> Successfully started `docker-machine` (label: homebrew.mxcl.docker-machine)
Check the status:
$ brew services list
Name Status User Plist
docker-machine started name /Users/name/Library/LaunchAgents/homebrew.mxcl.docker-machine.plist
Create a default instance using the following command:
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox --virtualbox-memory 8192 default
Please refer to this link for some detail instruction.
Every time you created a new terminal window, and before you execute any command of 'docker *', you are supposed to run the following command:
eval $(docker-machine env default)
This command will append some environment variables to your current sessions.
FAQ
Q: Can not connect to docker
Error Message:
$ docker ps -a
Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?
Please make sure you have already started your session.
Q: Start docker-machine Failed, Can Not Get IP Address
The default manager by vbox is conflict with vpn AnyConnect, if you are using it, just disconnect it.
Q: Invalid Active Developer Path
xcrun: error: invalid active developer path (/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools), missing xcrun at: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/xcrun
Error: Failure while executing: git config --local --replace-all homebrew.analyticsmessage true
try xcode-select --install and then brew update, brew upgrade, and brew doctor again
Q: Where are the data for the images and hard disks?
They are in $HOME/.docker